GCSE Physics breakdown: topics, learning objectives & sample questions
By Atom | Aug 15, 2025, 10:34 AM
Contents
From understanding how forces shape motion to exploring the laws that govern electricity and energy, GCSE Physics gives students a powerful framework for interpreting the world around them.
What this post covers:
Full topic list for GCSE Physics (AQA, Edexcel and OCR)
Key learning objectives for each topic
Sample exam-style questions to support revision
Why Physics matters for GCSE success
GCSE Physics develops essential skills in calculation, logical thinking and data interpretation. Success in Physics often comes down to understanding and applying the core principles in unfamiliar contexts, a key requirement for high marks and future Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) study.
Whether students go on to study engineering, medicine, environmental science or technology, a good understanding of Physics helps them take the next step in their education and builds useful skills like problem-solving, critical thinking and working with numbers.
Exam boards and specification overview
GCSE Physics is studied in two formats:
As part of Combined Science (2 GCSEs across Biology, Chemistry and Physics)
As a separate GCSE (Triple Science), giving students one full GCSE in Physics Combined Science vs Triple Science
Combined Science vs Triple Science
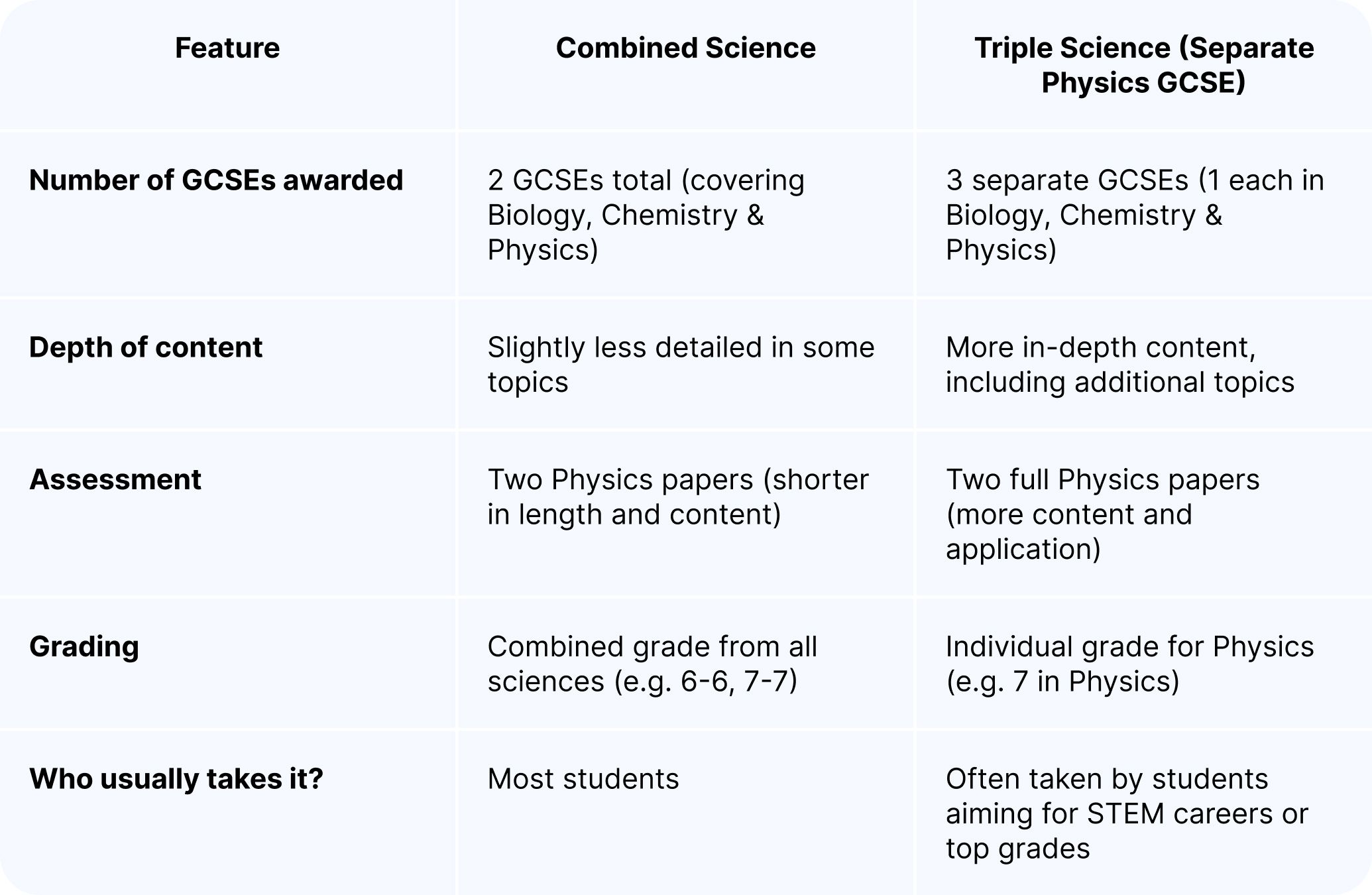
Triple Science students often study more advanced applications, such as momentum, space physics or thermal conductivity calculations.
This gives them more opportunities to score highly, but also requires deeper understanding and problem-solving skills.
Exam board overview
While the themes are consistent, each exam board organises the content slightly differently:
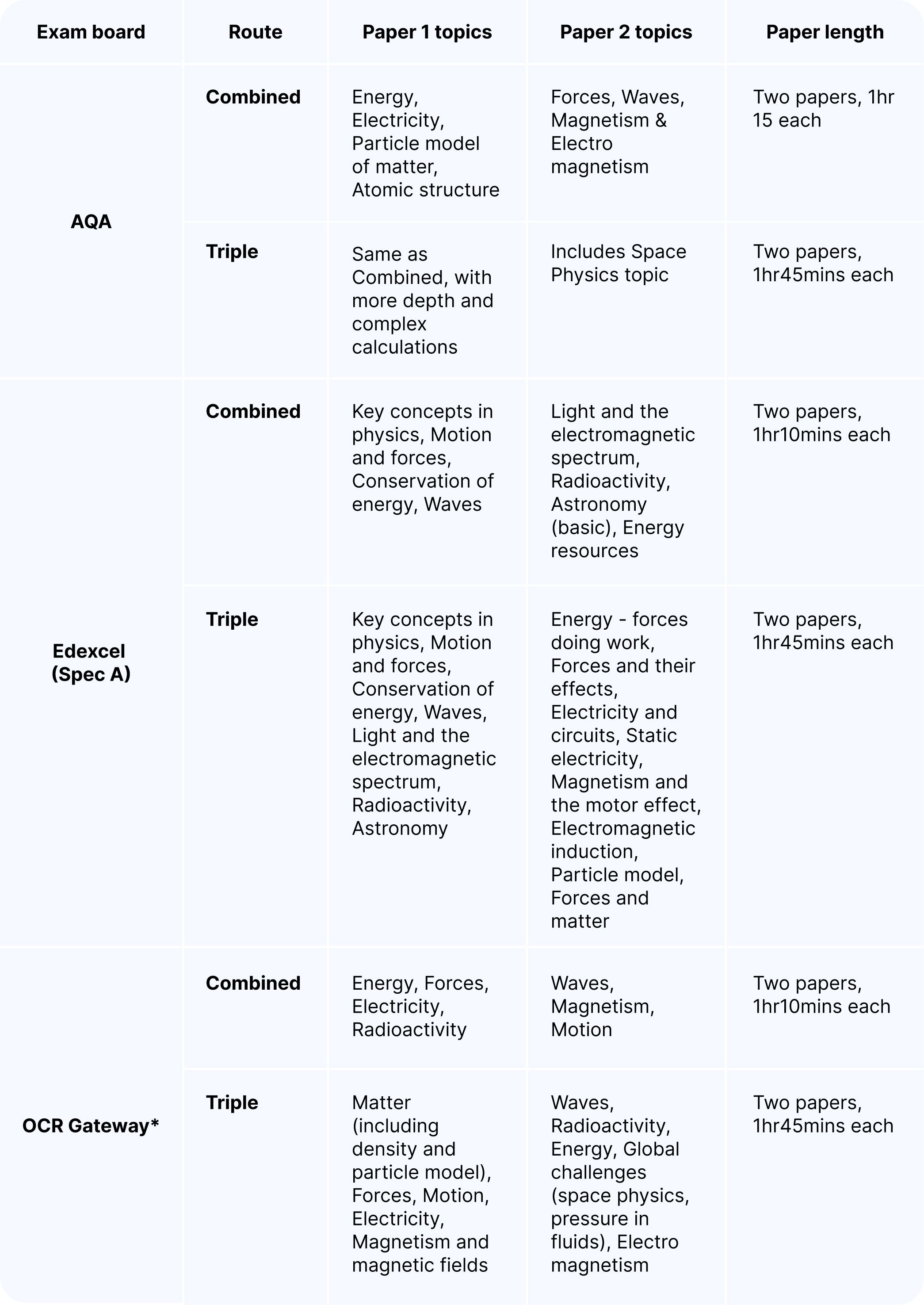
*OCR offers more than one pathway (e.g. Physics A: Gateway Science and Physics B: Twenty-First Century Science). The core content is very similar, but topics may be grouped differently and assessed in slightly different ways. Make sure to check with your teacher which pathway your school is using.
Physics key topics and learning objectives
1. Energy
Learning objectives:
Understand energy stores and transfers
Calculate efficiency and energy in systems
Analyse heating and insulation
Sample question:
Explain how insulation reduces energy loss in a house (4 marks)
2. Electricity
Learning objectives:
Identify circuit components and interpret circuit diagrams
Use Ohm’s Law and calculate resistance, power and energy
Understand mains electricity and safety
Sample question:
Calculate the current in a 230V, 2kW kettle (3 marks)
3. Particle model of matter
Learning objectives:
Describe changes of state and the particle model
Understand internal energy, specific heat capacity and latent heat
Apply gas pressure equations (Triple only)
Sample question:
Explain what happens to the internal energy of a substance when it melts (3 marks)
4. Atomic structure
Learning objectives:
Understand atomic models and nuclear structure
Explain radioactive decay, half-life and nuclear radiation uses
Evaluate the risks and safety of ionising radiation
Sample question:
Define the term half-life and explain how it is measured (4 marks)
5. Forces
Learning objectives:
Define scalar and vector quantities
Use Newton’s Laws, calculate force, acceleration and momentum
Interpret motion graphs and terminal velocity
Sample question:
A car accelerates from 10 m/s to 30 m/s in 5 seconds. Calculate the acceleration (2 marks)
6. Waves
Learning objectives:
Understand the properties of transverse and longitudinal waves
Calculate wave speed, frequency and wavelength
Describe reflection, refraction and the electromagnetic spectrum
Sample question:
Describe how a ripple tank can be used to investigate wave speed (4 marks)
7. Magnetism and electromagnetism
Learning objectives:
Describe magnetic fields and the motor effect
Understand electromagnets and transformers
Calculate force using F = BIL (Triple only)
Sample question:
Explain how a loudspeaker uses electromagnetism to produce sound (6 marks)
8. Space physics (Triple Science only)
Learning objectives:
Understand life cycles of stars, including black holes and red giants
Describe orbital motion and the expansion of the universe
Sample question:
Describe how a star much larger than the Sun ends its life (4 marks)
Tips for revision and exam preparation
A strong revision plan for GCSE Physics combines understanding key principles with regular, targeted practice. Here are some strategies that help students engage meaningfully with the subject and build exam confidence:
1. Break topics into manageable chunks
Physics spans a wide range of concepts, from forces and energy to electricity and waves. Divide revision into focused topics such as motion, magnetism or radiation, so students can concentrate on one idea at a time.
This approach helps prevent overwhelm and builds a stronger foundation across the specification.
2. Use active recall and self-testing
Effective Physics revision goes beyond re-reading notes. Use techniques like flashcards for key equations, definitions and units, or try explaining concepts aloud without notes. Regular self-testing strengthens memory recall and helps identify weak spots early.
3. Apply concepts through exam-style questions
Physics questions often present familiar concepts in unfamiliar contexts. Practising with exam-style questions throughout revision (not just at the end) helps students apply their knowledge, improve problem-solving skills and understand how marks are awarded.
4. Practise interpreting data and graphs
Data analysis is a key skill in GCSE Physics. Students should practise reading graphs, calculating gradients, and drawing conclusions from experimental data. These skills are especially important for required practicals and extended-response questions.
5. Start with the challenging topics
Areas such as forces in motion, energy transfers, or electromagnetism can be more demanding. Address these earlier in the revision process to allow time for repeated practice and clarification. Leaving these until later can create unnecessary pressure.
6. Use visual representations
Diagrams, circuit symbols, ray diagrams and motion graphs are central to Physics understanding. Encourage students to draw and label diagrams from memory, or to create flow charts that link processes (e.g. energy transfers in a system). Visual tools help clarify abstract ideas and improve retention.
7. Get comfortable with equations and units
Students need to know which formulas to memorise and how to rearrange them confidently. Practice should include identifying correct units, converting values, and checking final answers for accuracy. Building fluency with equations reduces anxiety and improves performance in calculation-heavy questions.
Final thoughts
With the right strategy and tools, GCSE Physics doesn’t need to be stressful. Focus on consistent revision, practise past questions, and remember small steps lead to big gains.
Don’t miss Atom’s GCSE giveaway!

Six months. Six epic prizes. Six chances to make the GCSE season unforgettable.
We’re launching Atom for GCSE prep in 2026, and to celebrate, over the next six months, we’re giving away thousands of pounds worth of prizes to help your child level up their GCSE revision.
Here’s a taste of what’s up for grabs:
The latest Apple tech, including an iPad Air, Vision Pro and more
Festival tickets for Boardmasters and Reading 2026
Europe interrail passes and £1,000 spending money
…and that’s just a few of the amazing prizes available.
Our first two winners have already taken home incredible prizes! Find out who they are and what they won in our latest giveaway update and keep an eye out for news of our November winner.
It’s free to join. UK only. Full T&Cs apply.
Contents
